Rights and Duties of Buyers and Sellers
Introduction
The Sales of Goods Act, 1930 outlines the rights and duties of both buyers and sellers in contracts involving the sale of goods. This Act plays a crucial role in regulating such transactions, ensuring they are fair, transparent, and legally sound. It is important to note that contracts under the Sales of Goods Act are also governed by the principles of the Indian Contract Act.
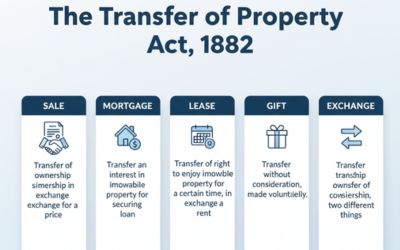
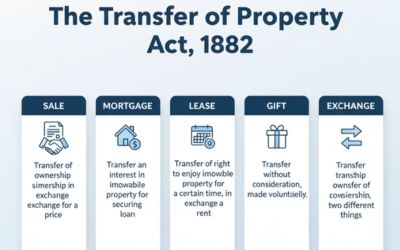
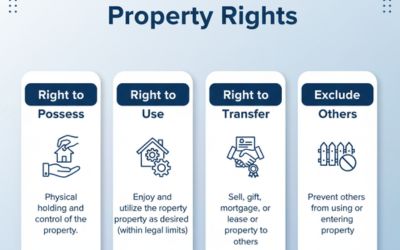
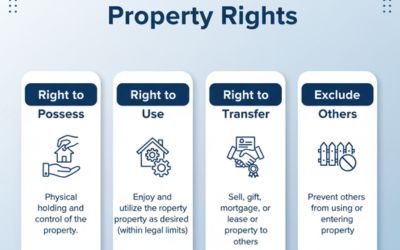
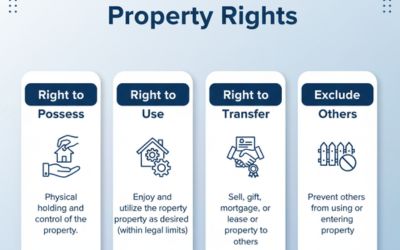
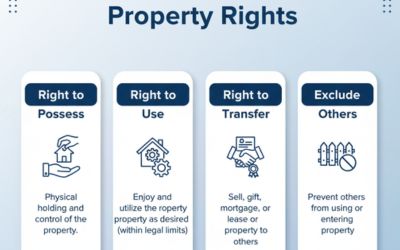
While the Transfer of Property Act addresses the rights and duties of buyers and sellers of immovable property, the Sales of Goods Act specifically deals with the rights and duties in the context of movable goods.
Who is a Buyer?
A buyer is an individual, organization, or entity that acquires goods or services in exchange for payment. In a commercial setting, a buyer is the party that initiates a transaction, expresses interest in a product or service, negotiates terms, and ultimately makes a purchase. Buyers can range from consumers purchasing goods for personal use to businesses acquiring raw materials or finished products for resale or production. Essentially, a buyer is anyone actively acquiring goods or services in a market transaction.
Who is a Seller?
A seller is an individual, organization, or entity that offers goods or services to potential buyers. In a commercial context, a seller supplies products or services and seeks to exchange them for monetary payment or other forms of value. The seller typically responds to buyer inquiries, negotiates terms, and completes the sale transaction. Sellers can be small business owners, manufacturers, retailers, or service providers. In essence, a seller is a party that actively provides goods or services in exchange for value in a market transaction.
Rights and Duties of Buyers
Rights of the Buyer
- Right to Delivery as per Contract: Buyers are entitled to receive goods in line with the contract’s terms. Sections 31 and 32 of the Act emphasize the buyer’s right to timely and exact delivery.
- Right to Reject Non-Conforming Goods: If the goods do not match the contract's description, quality, or quantity, the buyer can reject them. Section 37 safeguards this right.
- Right to Repudiate Contract for Unapproved Instalments: If the seller delivers goods in instalments without prior agreement, Section 38(1) allows the buyer to repudiate the contract.
- Right to Be Informed and Arrange Insurance: If goods are sent via sea, the seller must inform the buyer, enabling them to arrange insurance as per Section 39(3).
- Right to Examine Goods: Buyers have the right to inspect goods to ensure they meet the contract’s specifications, as outlined in Section 41.
- Right to Recover Price Paid: If the seller fails to deliver as agreed, the buyer can sue to recover the price paid.
- Right to Sue for Non-Delivery: Section 57 allows buyers to seek damages if the seller refuses to deliver the goods.
- Right to Specific Performance: Buyers can request the court to enforce the contract if the seller fails to fulfill their obligations.
- Right to Sue for Breach of Warranty or Condition: Sections 59 and 60 empower buyers to sue for damages if there’s a breach of warranty or a condition treated as such.
- Right to Claim Interest on Breach: If the seller breaches the contract and a refund is due, Section 61 allows the buyer to claim interest.
Duties of the Buyer
- Duty to Accept Delivery: Buyers must accept the goods when the seller is ready to deliver as per the contract (Section 31).
- Duty to Pay for Goods: Buyers are obligated to pay the agreed price for the goods.
- Duty to Apply for Delivery: Buyers must formally request delivery of the goods (Section 35).
- Duty to Demand Delivery at Reasonable Hours: Buyers should demand delivery at a reasonable time (Section 36(4)).
- Duty to Accept Instalments: If the contract allows, buyers must accept and pay for goods delivered in instalments (Section 38(2)).
- Duty to Bear Risk in Transit: If the goods are delivered to a different location, buyers assume the risk during transit (Section 40).
- Duty to Inform Seller of Refusal: If buyers reject the goods, they must inform the seller (Section 43).
- Duty to Take Delivery Promptly: Buyers must accept goods within a reasonable time after delivery (Section 44).
- Duty to Pay as Property Passes: Buyers must pay the price when ownership transfers (Section 55).
- Duty to Pay Damages for Non-Acceptance: If buyers refuse to accept the goods, they may have to pay damages (Section 56).
Rights and Duties of Sellers
Rights of the Seller
- Right to Retain Control of Goods: Sellers can retain control of the goods until certain conditions are met (Section 25(1)).
- Right to Assume Buyer’s Acceptance: Sellers may assume acceptance if the buyer does not reject the goods within a reasonable time (Section 24).
- Right to Deliver upon Buyer’s Request: Sellers must deliver goods only when formally requested by the buyer (Section 35).
- Right to Deliver in Instalments: If agreed upon, sellers can deliver goods in instalments (Section 39(1)).
- Right to Lien and Retain Possession: Sellers can retain goods until full payment is received (Section 47(1)).
- Right to Stop Goods in Transit: If the buyer fails to pay, sellers can stop the goods during transit and resume possession (Sections 49(2) and 50).
- Right to Resell Goods: If the buyer defaults, sellers can resell the goods and claim damages (Section 54).
- Right to Withhold Delivery: Sellers can withhold delivery if ownership has not yet passed to the buyer (Section 46(2)).
- Right to Sue for Price: If the buyer fails to pay after the property has passed, sellers can sue for the price (Section 55).
Duties of the Seller
- Duty to Transfer Property: Sellers must arrange for the transfer of ownership to the buyer.
- Duty to Ensure Goods Conform to Contract: Sellers must provide goods that meet the contract’s terms.
- Duty to Pass Clear Title: Sellers must pass an absolute and effective title to the buyer.
- Duty to Deliver as per Contract: Sellers must deliver goods according to the contract’s terms (Section 31).
- Duty to Make Goods Deliverable: Sellers must ensure goods are in a deliverable state before delivery.
- Duty to Deliver on Time: Sellers must deliver goods within the specified or reasonable time (Sections 36(2) and (4)).
- Duty to Cover Delivery Expenses: Sellers must bear delivery costs up to the point of making the goods deliverable (Section 36(5)).
- Duty to Deliver the Agreed Quantity: Sellers must deliver the exact quantity as per the contract (Section 37(1)).
- Duty to Deliver Instalments as Desired by Buyer: Sellers must deliver in instalments if the buyer desires (Section 38(1)).
- Duty to Arrange Insurance: Sellers must arrange for insurance during transit (Section 39(2)).
- Duty to Inform Buyer of Sea Route: Sellers must inform the buyer if goods are sent via sea, allowing for insurance arrangements (Section 39(3)).
Share
Related Post
Tags
Archive
Popular & Recent Post














































































Comment
Nothing for now